Introduction
The Arduino Nano 33 IoT is a compact yet capable board designed for modern connected electronics. It combines efficient processing with stable wireless performance, making it a strong choice for small IoT builds. Its structure supports practical experimentation, whether you’re testing sensors or linking devices to the internet. The board includes features that simplify secure communication and cloud integration. Engineers often choose it as a reliable platform for learning and development because it fits into tight spaces while maintaining dependable operation. This board serves well in educational work, embedded experiments, and connected prototypes using IoT development board, ARM Cortex-M0+ microcontroller, Secure IoT communication, Low-power wireless module, and Built-in IMU sensor technologies.
Overview
The Arduino Nano 33 IoT offers a balance between computing ability, wireless connectivity, and footprint size. It includes Wi-Fi and BLE hardware for networking tasks and supports practical prototyping through simple coding workflows. Its SAMD21-based design suits small devices that need responsiveness and efficient energy use. The board works smoothly with the Arduino ecosystem, giving access to libraries, cloud tools, and online dashboards. For engineers, it simplifies wireless testing and secure device pairing without extensive configuration. Its layout supports structured experimentation in IoT systems, embedded applications, academia, and real-world development environments.
What Is Arduino Nano 33 IoT?
The Arduino Nano 33 IoT is a compact Development board built around the SAMD21 microcontroller series and integrated Wi-Fi module and Bluetooth LE hardware. It enables Wireless communication, sensor interfacing, and Cloud connectivity for a wide range of IoT applications. The NINA module handles Wi-Fi/BLE links, while the onboard ATECC608A security chip improves Security for authentication and encrypted sessions. It’s suited for Microcontroller for IoT projects that require small size with reliable network support.
Key Features
Arduino ecosystem compatibility
Nano form factor with low-power design
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity via NINA module
Built-in IMU sensor for IMU sensor data collection
SAMD21 board architecture for efficient processing
Arduino library support for cloud dashboards
Hardware Security chip for protected sessions
Designed for Wireless communication and Connected devices
Suitable for IoT beginner projects and advanced development
Technical Specifications
Microcontroller: SAMD21 ARM Cortex-M0+
Wireless: Wi-Fi, BLE (Bluetooth LE)
Crypto chip: ATECC608A security chip
IMU: 6-axis accelerometer + gyroscope
Operating voltage: 3.3V
Clock speed: 48 MHz
Flash memory: 256 KB
SRAM: 32 KB
USB power or external regulated supply
Supports OTA (Over-the-air updates)
Integrated Wireless protocol integration options
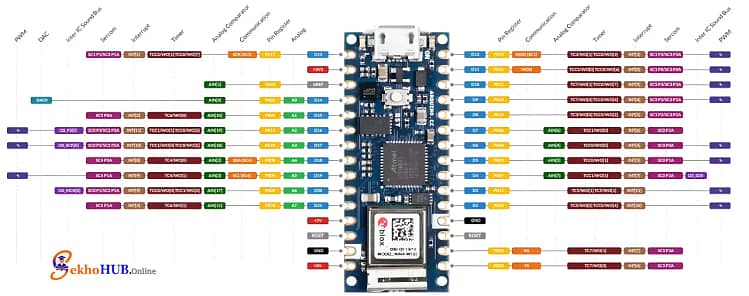
Pinout Explanation
Power Pins: 3.3V, 5V input (VUSB), GND
Digital Pins: Standard I/O with interrupts
PWM Pins: For motor and LED control
Analog Pins: Sensor interfacing
UART/SPI/I2C: Communication ports
IMU Pins: Internal access through libraries
Reset Pin: Hardware reset
Arduino Nano 33 IoT Pinout
Board Architecture
SAMD21 microcontroller series handling core tasks
NINA Wi-Fi module managing Wireless communication
BLE functions for device-to-device links
ATECC608A security chip for Arduino secure authentication
Integrated Sensor suite for motion tracking
Power regulation for stable operation
Designed for Embedded system design, Lightweight IoT hardware, and IoT sensor networks
Getting Started
You’ll need the following components to get started:
| Component | Quantity | Buy Link |
|---|---|---|
| Arduino Nano 33 IoT | 1 | Add link |
| Micro USB Cable | 1 | Add link |
| Breadboard | 1 | Add link |
| Jumper Wires | As required | Add link |
| Basic Sensor (DHT22, LM35, etc.) | 1 | Add link |
Programming the Arduino Nano 33 IoT
Programming is done through the Arduino IDE, where you select the board and port, load an example, and upload it. You can work with coding examples for Nano 33 IoT, manage Wireless communication, collect IMU sensor data, and test Arduino cloud connection. The board supports How to program Arduino Nano 33 IoT with Wi-Fi, BLE, sensor reading, cloud dashboards, and OTA capability.
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Usage
Use onboard Wi-Fi module for cloud dashboards
Apply Wi-Fi setup on Nano 33 IoT templates
Test Bluetooth LE functions for device pairing
Handle Arduino Nano 33 IoT Wi-Fi setup and Arduino Nano 33 IoT Bluetooth example
Secure sessions using Arduino secure authentication
Power Management
USB 5V input or regulated 3.3V
Battery operation supported
Sleep modes for Power optimization for IoT
Lower consumption during idle states
Measuring Arduino Nano 33 IoT power usage for long-term deployments
Common Issues & Troubleshooting
Board not detected → Check drivers and cable
Wi-Fi not connecting → Recheck SSID and encryption
BLE device not appearing → Restart module
Sensor not reading → Verify wiring and voltage
Sketch won’t upload → Reset board before upload
Applications
Portable monitoring devices
Weather and environmental measurement
Smart home modules
Wearable prototypes
Cloud-connected project boards
Wireless sensor integration
Low-power field devices
Educational IoT systems
FAQs
What is Arduino Nano 33?
A compact IoT-ready board based on the SAMD21 MCU with Wi-Fi, BLE, and an onboard IMU.
What is the use of Arduino Nano 33 IoT?
It is used for IoT applications requiring wireless communication, cloud connectivity, and secure data handling.
Does the Arduino Nano 33 IoT have WiFi?
Yes, it includes Wi-Fi through the onboard NINA module.
Do Arduino Nano 33 IoT have gyrometers in them?
Yes, the IMU contains a built-in accelerometer and gyroscope.
Which is better, ESP32 or Arduino Nano?
ESP32 offers more processing power, while the Nano 33 IoT provides stronger integration with Arduino’s cloud and security features.
How long will a 9V battery power an Arduino?
Typically a few hours, depending on load and wireless usage.
Conclusion
The Arduino Nano 33 IoT combines practical processing capability, stable wireless functions, and a compact design that suits both hobbyists and engineers. With built-in security and sensor resources, it handles a variety of modern IoT scenarios without requiring complex setup. Its library ecosystem, cloud support, and low-power features make it a dependable choice for learning, prototyping, and deploying connected systems. Whether used for sensor networks, small appliances, or cloud dashboards, it provides a strong foundation for structured IoT development.