A Microphone Amplifier Circuit is the first building block in any audio system where weak voice signals need proper boosting. A microphone produces a very low-level signal, which cannot directly drive an amplifier or power stage. This is where a carefully designed audio preamplifier circuit becomes essential. In practical designs, engineers focus on low noise mic amplifier performance, stable gain, and clean signal handling. Using a transistor microphone amplifier with proper biasing ensures reliable operation. For hobbyists and professionals alike, a compact DIY microphone preamp helps achieve clear audio without distortion in small audio systems.
Overview
This Microphone Amplifier Circuit is designed as a compact small signal audio amplifier that boosts weak mic signals to a usable level. The circuit uses a single-transistor topology, making it simple, affordable, and easy to troubleshoot. By using proper signal conditioning, a balanced input impedance, and a well-chosen coupling capacitor, the circuit delivers stable amplification with improved audio clarity. The design is suitable for direct mounting on a microphone preamp PCB, allowing it to integrate neatly with a power amplifier. Overall, this audio amplification circuit is ideal for beginners and DIY builders looking for clean and reliable microphone signal amplification.
Components Required
| Component | Specification | Quantity | Buy Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistor | 560 Ω, ¼ W | 1 | Buy Link |
| Resistor | 4.7 kΩ, ¼ W | 1 | Buy Link |
| Resistor | 1 MΩ, ¼ W | 1 | Buy Link |
| Resistor | 47 kΩ, ¼ W | 2 | Buy Link |
| Capacitor | 104 ceramic (0.1 µF) | 2 | Buy Link |
| Capacitor | 403 ceramic (0.04 µF) | 1 | Buy Link |
| Capacitor | 100 µF / 25 V electrolytic | 1 | Buy Link |
| Transistor | BC548 NPN transistor | 1 | Buy Link |
| Socket | Microphone socket | 1 | Buy Link |
| PCB | Printed circuit board | 1 | Buy Link |
| Soldering paste / flux | — | As required | — |
| Solder wire | — | As required | — |
BC548 NPN Transistor
The BC548 NPN transistor is widely used in low-power audio and preamplifier circuits. It offers stable transistor gain, low noise, and predictable performance for microphone applications. Its characteristics make it ideal for mic input stage circuit designs where clean signal amplification is required.Learn more
Circuit Diagram
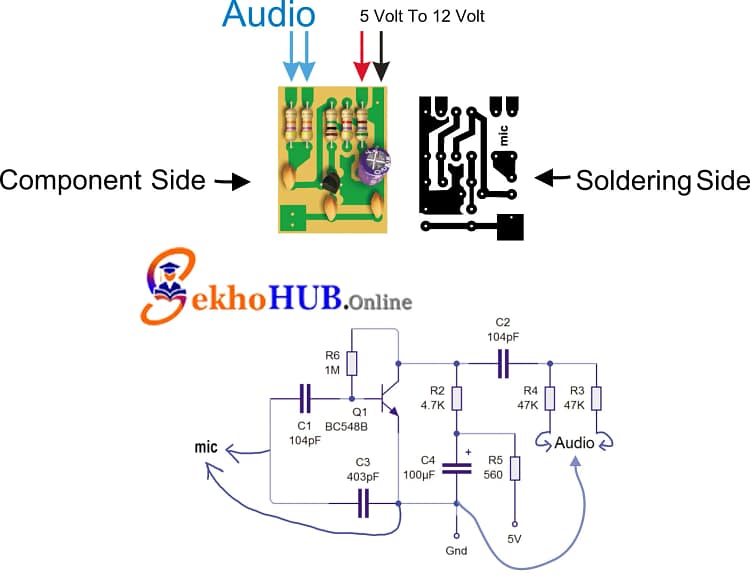
The microphone amplifier circuit diagram shows a single transistor mic amplifier configuration. An electret microphone module feeds the base through a coupling capacitor, while a bias resistor network sets the operating point. The collector output provides amplified audio with controlled output signal level. Proper grounding in audio circuits and power supply filtering help maintain a good signal-to-noise ratio.
PCCB Layouts
Build Guide Step-by-Step
Step 1
First, install the 560-ohm resistor.
Now install the 4.7K resistor.
Then place the 1-meg resistor on the PCB.
Step2
Next, install two 47K resistors for the audio path. You may replace them with 22K, 56K, or 68K depending on desired gain and availability.
Step3
Now install the two 104 ceramic capacitors.
After that, insert the BC548 microphone amplifier transistor (BC148 also works).
Step4
Install the 403 ceramic capacitor (0.04 µF).
Then install the 100µF, 25V electrolytic capacitor with correct polarity.
Step5
Cut the PCB to size if required.
Apply soldering paste and solder all components carefully.
Step6
Finally, connect the microphone preamp board to the amplifier. You may solder it directly to the microphone socket or connect it using wires if mounted separately.
Applications
microphone audio circuit for small amplifiers
mic amplifier circuit in PA systems
audio pre amplifier stage for DIY speakers
mic input amplifier for recording projects
small audio amplifier input section
Educational DIY microphone amplifier circuit projects
FAQs
What is a microphone amplifier?
A microphone amplifier boosts a very weak mic signal to a usable voltage level.
How to make a simple audio amplifier circuit?
Use a transistor, resistors, capacitors, and proper biasing to form a basic preamp circuit.
What is a microphone in a circuit?
A microphone converts sound waves into a small electrical audio signal.
How does a mic amp work?
It uses controlled transistor amplification to increase signal strength while reducing noise.
Do microphones need an amplifier?
Yes, most microphones require a preamplifier to raise signal levels.
What is the 3 to 1 mic rule?
It helps reduce phase issues by spacing microphones three times farther apart than the source distance.
Conclusion
This Microphone Amplifier Circuit offers a practical balance between simplicity and performance. With minimal components and a proven transistor microphone amplifier design, it delivers clean amplification suitable for many audio projects. Proper component placement, grounding, and PCB layout ensure stable operation and long-term reliability. Whether you are learning audio electronics or building a compact sound system, this circuit is an excellent starting point.

