What Are Filters in Electronics?
[Sekhohub.online]
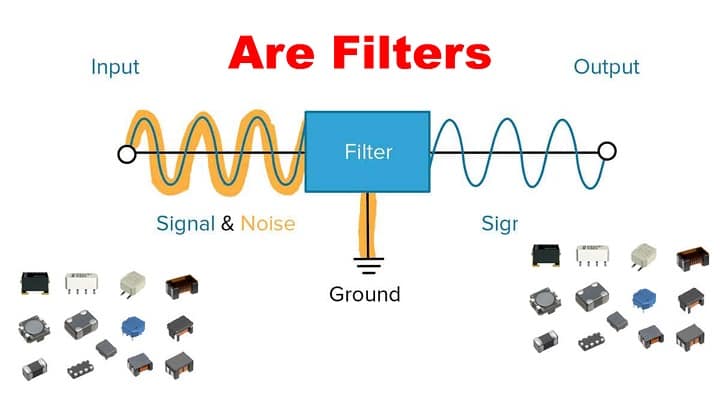
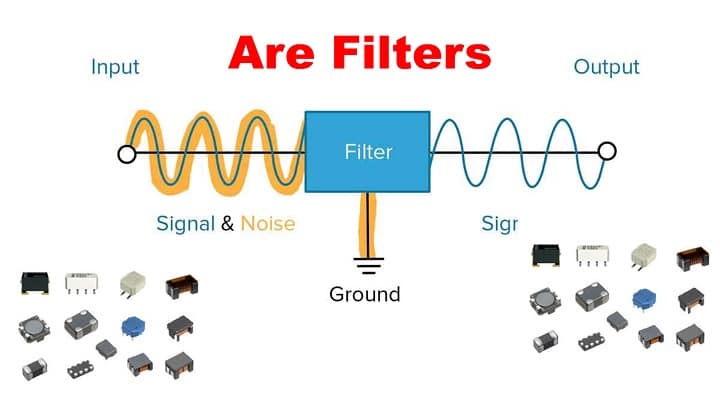
Filters are electronic circuits that allow certain frequencies to pass while blocking or attenuating others. They are essential in signal processing, communication systems, audio electronics, and power supplies.
Simple Definition:
A filter selects the frequencies you want and removes the ones you don’t.
Example: In a speaker system, a filter ensures bass goes to the subwoofer and high notes go to the tweeter
Types of Filters (Based on Frequency Response):
Filter Type Function
Low-Pass Filter (LPF) Passes low frequencies, blocks high ones
High-Pass Filter (HPF) Passes high frequencies, blocks low ones
Band-Pass Filter (BPF) Passes a range of frequencies, blocks others
Band-Stop Filter (BSF) Blocks a specific range, passes the rest
Notch Filter A narrow band-stop filter (very specific reject band)
⚙️Types Based on Components:
Passive Filters:
Use resistors (R), capacitors (C), inductors (L)
No power supply needed
Lower gain and flexibility
Active Filters:
Use op-amps, transistors, and R and C
Require power
Can amplify signals
More control and better performance
Filter Circuit Examples:
Low-Pass Filter (RC)
Allows low frequencies to go through
Blocks high frequencies above a cutoff frequency fcf_c
fc=12πRCf_c = \frac{1}{2\pi RC}
Applications of Filters:
✅ Audio systems – separate bass/mid/treble
✅ Radio receivers – select desired frequency band
✅ Power supplies – remove ripple (noise filtering)
✅ Medical devices—filter out unwanted bio-signals
✅Sensors—remove high-frequency noise