7 Powerful Things You Must Know About the TTP223 Touch Sensor
The TTP223 touch sensor is a popular capacitive touch detection module widely used in DIY electronics, home automation, and embedded projects. It eliminates the need for traditional push buttons by detecting a finger’s presence through changes in capacitance. This module works on 2V–5.5V, outputs a digital HIGH when touched, and is compatible with both Arduino and ESP32. In this guide, we’ll cover the introduction, working principle, pinout, and specifications of the TTP223 touch sensor.
You’ll also learn about its touch range, output voltage behavior, and real-world applications. To help you get started, we’ve included a complete bill of materials (BOM), a step-by-step Arduino project, and circuit diagram explanation. Whether you’re building hidden switches, smart lamps, or automation systems, the TTP223 touch sensor offers a modern, durable, and reliable solution. This 2500+ word guide covers everything you need.
Introduction – The Rise of Capacitive Touch in Electronics
Mechanical push buttons have served electronics well for decades. However, they come with inherent drawbacks such as:
Physical wear and tear due to moving parts
Contact bounce that requires extra filtering
Dust, dirt, and moisture susceptibility
Bulky designs compared to sleek alternatives
This is where capacitive touch technology steps in. With the help of ICs like the TTP223, electronic devices can detect touch without requiring any physical button press.
The TTP223 touch sensor has become one of the most widely used touch detection modules in DIY electronics, offering:
Compact size
Low power consumption
Simple digital output interface
Compatibility with microcontrollers like Arduino, ESP32, and Raspberry Pi
In short, it replaces mechanical buttons with modern, touch-based interactivity, making your projects feel futuristic.
Working Principle of the TTP223 Touch Sensor
The TTP223 IC continuously monitors the capacitance of its sensor pad.
Normal State (No Touch):
The pad has a baseline capacitance. Output pin remains LOW (0V).Touch Detected:
When a human finger approaches, the capacitance increases slightly.
The IC detects this change and sets its output pin HIGH.Modes of Operation:
Momentary Mode: Output remains HIGH only while finger is touching.
Toggle Mode: Touch once to turn HIGH, touch again to turn LOW.
This ability to detect through non-metallic surfaces like acrylic, plastic, or glass makes the module ideal for hidden switches in home automation.
Pinout & Technical Specifications
The TTP223 module typically comes as a small breakout board with 3 pins:
VCC → Supply voltage (2V – 5.5V)
GND → Ground connection
OUT → Digital output (HIGH when touched, LOW when idle)
Technical Specs:
Operating Voltage: 2.0 – 5.5V DC
Supply Current:
Standby mode: ~1.5 µA (ultra-low power)
Active mode: ~3.5 mA
Output Voltage: Equal to supply voltage (3.3V or 5V depending on input)
Output Type: Digital (TTL logic compatible)
Response Time: < 60 ms typical
Touch Surface Material: PCB copper pad (works through non-metallic overlays)
Dimensions: 15 × 11 mm (typical breakout board)
This simplicity makes the TTP223 a “plug and play” solution for touch detection.
Touch Range of TTP223
The touch detection range of the TTP223 depends on pad size and overlay thickness.
Direct Touch: 0–2 mm (best sensitivity)
Plastic/Acrylic Overlay: Up to ~5 mm thickness
Glass Overlay: ~2–4 mm thickness
Metal Surface: Not supported (metal blocks capacitive sensing)
Thus, while the TTP223 isn’t designed for long-range sensing, it’s perfect for short-range human touch interaction.
Output Voltage Details
The OUT pin of the TTP223 outputs a clean digital logic signal:
Logic HIGH: ~VCC (3.3V or 5V depending on supply)
Logic LOW: ~0V
Examples:
If VCC = 5V → HIGH = 5V
If VCC = 3.3V → HIGH = 3.3V
This makes it directly compatible with:
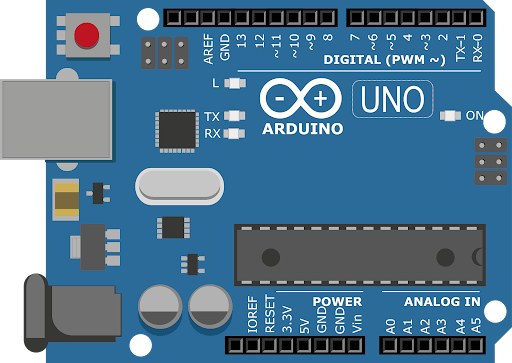
Arduino UNO (5V logic)
ESP32 / Raspberry Pi (3.3V logic)
No level shifter is needed, making integration straightforward.
Bill of Materials (BOM) – TTP223 Touch Sensor Project
| Component | Quantity | Description | Click & Buy |
|---|---|---|---|
| TTP223 Touch Sensor Module | 1 | Capacitive touch sensor | Click & Buy |
| Arduino UNO | 1 | Microcontroller board | Click & Buy |
| Breadboard | 1 | For circuit prototyping | Click & Buy |
| Jumper Wires | 10 | Male-to-male wires | Click & Buy |
| LED | 1 | Output indicator | Click & Buy |
| 220Ω Resistor | 1 | For LED current limiting | Click & Buy |
| USB Cable | 1 | Arduino connection | Click & Buy |
Circuit Diagram & Explanation
Connections:
TTP223 VCC → Arduino 5V
TTP223 GND → Arduino GND
TTP223 OUT → Arduino Digital Pin 7
LED → Arduino Pin 13 → Resistor → GND
Operation:
Touching the pad sets OUT HIGH.
Arduino detects HIGH on pin 7.
Arduino turns ON LED connected at pin 13.
Releasing touch switches LED OFF (in momentary mode).
This simple setup proves how easy the TTP223 is to integrate.
Step-by-Step Guide – Example
Here’s a simple Arduino sketch:
How to Test:
Upload the code.
Open Serial Monitor at 9600 baud.
Touch the TTP223 pad → LED glows and “Touch Detected!” prints.
Release → LED switches OFF.
This demonstrates momentary touch detection. With a small modification, you can make it toggle like a button.
Applications & Use Cases
The TTP223 touch sensor is used widely in:
Home Automation → Hidden wall switches, smart lighting controls
DIY Lamps → Touch to switch ON/OFF
Consumer Electronics → Touch-controlled toys & gadgets
Smart Furniture → Embedded in desks or mirrors for hidden control
Wearables → Low-power input for compact devices
Security Systems → Secret touch switches for access
Its low power consumption also makes it perfect for battery-powered projects.
FAQs – TTP223 Touch Sensor
Q1: What is the TTP223 touch sensor?
It is a capacitive touch detection module that replaces mechanical buttons with touch-sensitive input.
Q2: What is the touch range of TTP223?
Typically up to 5 mm depending on the surface material and thickness.
Q3: What is the output voltage of TTP223?
It matches the supply voltage: ~3.3V or 5V.
Q4: Can I use TTP223 with ESP32 or Raspberry Pi?
Yes, it works perfectly with 3.3V logic.
Q5: Can TTP223 detect touch behind glass or acrylic?
Yes, up to ~5 mm thickness for plastic/acrylic and ~2–4 mm for glass.
Q6: Does TTP223 require calibration?
No, it is auto-calibrated at power-up.
Q7: Is the sensor waterproof?
Not fully waterproof, but it can sense through non-metallic covers to protect it.
Final Thoughts
The TTP223 touch sensor is a robust, low-cost, and versatile alternative to traditional buttons. With its low power consumption, easy wiring, and Arduino compatibility, it has become a favorite for hobbyists and engineers alike.
Whether you’re building smart lamps, hidden switches, or advanced automation projects, this module adds a modern, sleek, and durable touch interface to your designs.